Are you a hepatitis B patient living in the United States? Are you taking entecavir or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) to help manage your hepatitis B infection? Thanks to the Hepatitis B Foundation’s new strategic partnership with Rx Outreach – America’s largest fully licensed, non-profit, mail order pharmacy and Patient Assistance Program – you may be able to receive your medication for less than 5% of the average retail price!
Each year, we answer thousands of national and international phone calls, emails, and social media messages from people who have been impacted by hepatitis B. Over the past year, we have seen a significant increase in calls regarding access to medication. The majority of those calls have been from people living in the United States. The ability to access medications is more than just having them available at a local pharmacy – it is about the price as well.
In the United States, life-saving generic treatments can cost more than $830 a month on average. As treatments are typically taken for several years after a person begins, paying such high monthly out-of-pocket costs simply isn’t an option for most people. That’s why we partnered with Rx Outreach to increase patient accessibility to life-saving hepatitis B medications.
We believe that affordable treatments should be low-cost and widely available to everyone who needs them. Hepatitis B antiviral treatments need to be taken daily in order to be effective, and a lack of affordable options force some individuals who are living with chronic hepatitis B to avoid diagnosis and treatment, to stop taking medication or to only take it sporadically, which increases their risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer. Our new partnership can help eliminate the need for such potentially harmful actions by providing the same medication at a much lower cost than retail pharmacies, pharmaceutical companies, and insurance plans can offer.
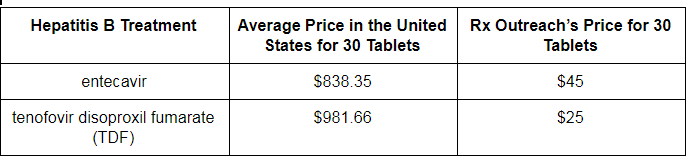
Rx Outreach provides a 30-day supply of entecavir and TDF – two of the most effective, common, and preferred treatments – through the mail. Interested individuals can enroll in the program with 3 simple steps. If you need to transfer your prescription from another pharmacy, you can do that too!
Eligibility Requirements:
Eligibility is based upon household income, not on insurance status or prescription drug coverage. To be eligible for Rx Outreach’s pricing, please review the chart below or you can check your eligibility here. If it appears that you do not qualify but you believe that you should, you can also call Rx Outreach and a representative will assist you.
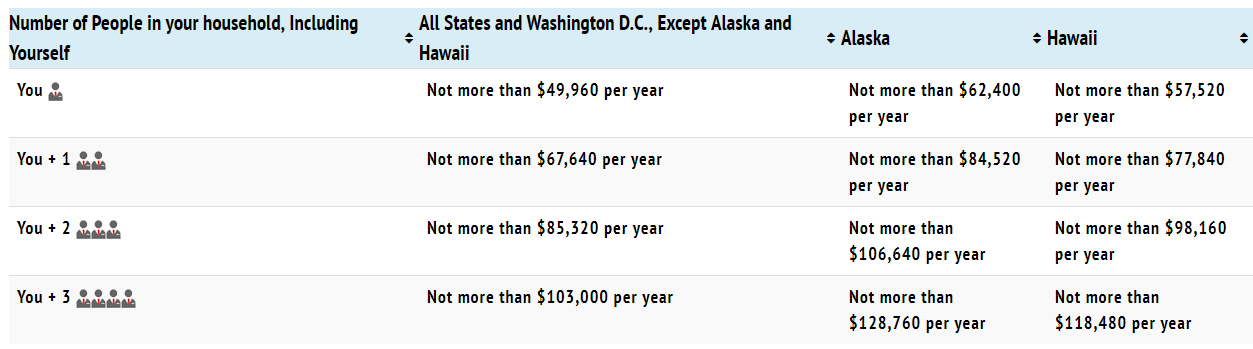
Our partnership with Rx Outreach will help to fill a gap in access to affordable medication and help to lessen the burden of one of the many forms of discrimination that those living with hepatitis B must face. It offers more than 1,000 medication strengths at affordable prices. Since 2010, Rx Outreach has saved people in need more than $662 million on their prescription medication.

 America to help raise money a
America to help raise money a Triathlon in Minnetonka, Minnesota – his first of six races this summer. In just under an hour and a half he accomplished: swimming more than 100 yards, biking 15 miles, and running 3 miles!
Triathlon in Minnetonka, Minnesota – his first of six races this summer. In just under an hour and a half he accomplished: swimming more than 100 yards, biking 15 miles, and running 3 miles! It comes down to factors, such as the type of sexual activity partners engage in, the viral load (HBV DNA) of the infected partner, and who is on the receiving end of infectious body fluids, especially blood (which contains the most virus), and semen.
It comes down to factors, such as the type of sexual activity partners engage in, the viral load (HBV DNA) of the infected partner, and who is on the receiving end of infectious body fluids, especially blood (which contains the most virus), and semen.