Little is known about the prevalence of hepatitis B and delta viruses (HBV/HDV) among people who use drugs (PWUD). Despite being a high-risk population, awareness of these viruses is still low among both community members and healthcare providers. Two recent studies conducted in Philadelphia, which were led by the Hepatitis B Foundation in partnership with Prevention Point Philadelphia, highlight different aspects of this ongoing public health concern. The first identified barriers to screening, prevention and linkage to care, while the other aimed to dismantle those barriers.
The first study explored the obstacles to HBV and HDV prevention, diagnosis and follow-up care. The study evaluated current knowledge levels and identified the needs and preferences of both people who use drugs and providers that serve them. Data was collected through an anonymous online provider-focused survey, and interviews were conducted with community members, and both medical and non-medical staff from different harm reduction settings in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Interviews with key informants revealed that:
- 48% of interviewed providers reported confusion about insurance coverage as a barrier to HBV screening.
- 45% of providers mentioned the need to address and prioritize other pressing health needs, as a challenge to conducting HBV screening.
- 52% of providers noted patient hesitancy as a barrier to HBV vaccination.
- 39% of providers identified the need to administer multiple doses as a challenge for completing the HBV vaccination series.
- 62% of providers reported low knowledge of HDV tests as a barrier to HDV testing.
- 31% of providers indicated complexity of guidelines as a challenge in HDV testing.
Overall, awareness of HBV and HDV in the community, and among staff and health care workers was low, and stigma related to drug use and harm reduction was a significant barrier to care. There is an urgent need to address this issue in a non-judgemental and non-stigmatizing way that is clear, factual and empowering. Continued financial and political support for harm reduction organizations is essential for improving health care access for people who use drugs. More efforts are needed to overcome barriers to vaccination, testing and linkage to care to create better health outcomes and ultimately increase the quality of life of people who use drugs.
The second study aimed to assess the prevalence of HBV and HDV and enhance access to care among people who use drugs, through a harm reduction organization (HRO) in Philadelphia. Participants first completed a demographic survey to help researchers gather information about their backgrounds and lifestyles, and to improve understanding of HBV and HDV risk factors within the community. Participants were then screened for HBV, and if they tested positive for certain HBV markers, they were automatically tested for hepatitis delta.
Of the 498 participants:
- 25.3% did not have hepatitis B immunity.
- 52.6% had been vaccinated against HBV.
- 17.9% had recovered from a past HBV infection.
- 2.2% tested positive for isolated HBV core antibody.
- 2.0% tested positive for HBV surface antigen.
- 0.2% tested positive for HDV antibody.
- 10% of those who were living with an active HBV infection had an HBV/HDV coinfection.
This study found that rates of current HBV infection in this community were nearly three times greater than in the general U.S. population, and the 10% coinfection rate of HDV is also significantly higher. Risk factors associated with a positive HBV status included a history of incarceration, experiences with homelessness and transactional sexual encounters. These findings highlight the prevalence of hepatitis B and D in this population. These viruses pose serious and critical public health concerns and remain under-prioritized among people who use drugs. Consistent and robust screening, vaccination, and linkage to care efforts can positively impact health outcomes for this community. Approving a hepatitis B point-of-care test (so that people who get tested can get results almost immediately), support in the form of funding and policy to allow HROs to provide full healthcare services, and adequate insurance coverage for vaccines can contribute to positive outcomes for hepatitis B and D diagnosis, prevention and treatment. These recommendations can advance elimination efforts, lower mortality, increase quality of life and center the health and needs of people who use drugs.
References
- Zovich, B., Freeland, C., Moore, H. et al. Identifying barriers to hepatitis B and delta screening, prevention, and linkage to care among people who use drugs in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. Harm Reduct J 21, 199 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12954-024-01117-4
- Zovich, B., Freeland, C., Moore, H., Sapp, K., Qureshi, A., Holbert, R., Zambrano, J., Bhangoo, D., Cohen, C., Hass, R. W., & Jessop, A. (2024). Dismantling Barriers to Hepatitis B and Delta Screening, Prevention, and Linkage to Care among the PWUD Community in Philadelphia. Viruses, 16(4), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040628
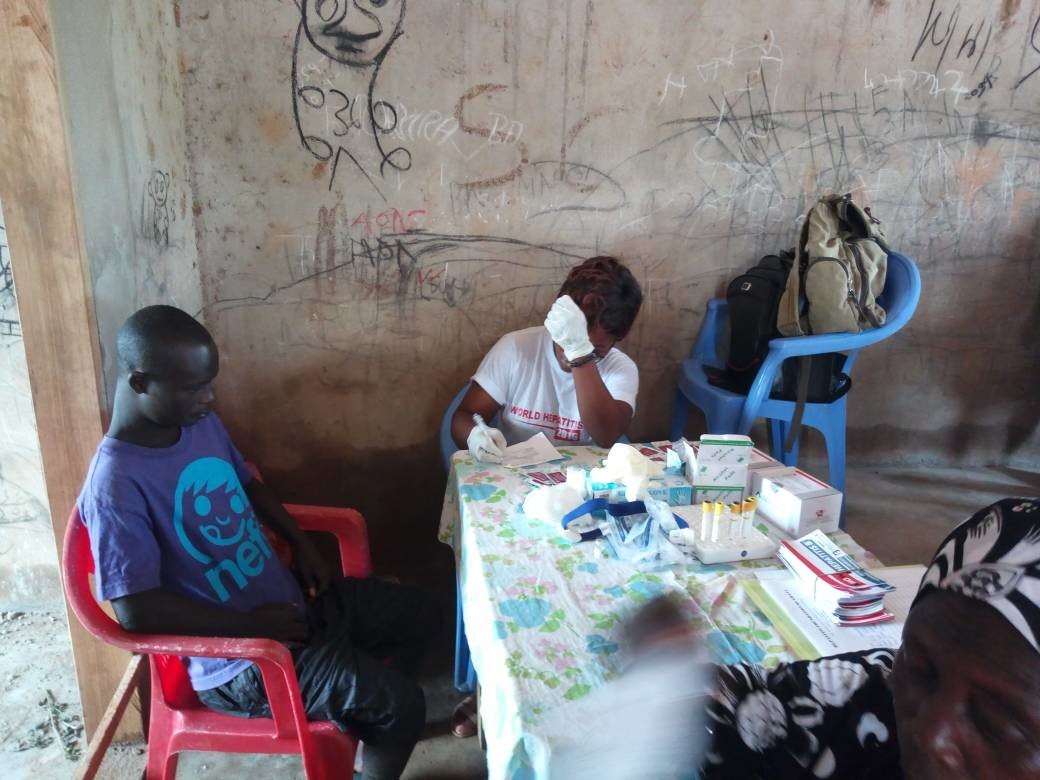





 Hepatitis B free screening and education were held at Ketu South, a community in the Volta region. A total of 244 persons were screened for hepatitis B. In all, 6 people tested positive. They were counselled and referred to the district hospital for proper care and treatment.
Hepatitis B free screening and education were held at Ketu South, a community in the Volta region. A total of 244 persons were screened for hepatitis B. In all, 6 people tested positive. They were counselled and referred to the district hospital for proper care and treatment.
 This special event began with a health walk through the streets in the Sekondi Komfoase area and followed with a hepatitis health talk and screening. Most of the people were afraid to come and do the hepatitis B and C tests because of some common perceptions on the radio and TV. I was able to share my family story with them, and that helped some of them come forward to do the test. The screening continued the next day at Home Church in Takoradi. Overcoming misperceptions about hepatitis B is very challenging – but we were able to screen179 persons, and are following up with all of those who tested positive.
This special event began with a health walk through the streets in the Sekondi Komfoase area and followed with a hepatitis health talk and screening. Most of the people were afraid to come and do the hepatitis B and C tests because of some common perceptions on the radio and TV. I was able to share my family story with them, and that helped some of them come forward to do the test. The screening continued the next day at Home Church in Takoradi. Overcoming misperceptions about hepatitis B is very challenging – but we were able to screen179 persons, and are following up with all of those who tested positive.