 Your liver specialist has informed you that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection, and that he wants to run additional blood work so he can learn more about your HBV. Some of this blood work may need to be repeated over a period of time, but over the next 6 months or so, your doctor will determine whether or not you are a good candidate for treatment. Regardless, he will definitely want to continue monitoring. Remember, treatment is important, but rarely an emergency, so be patient.
Your liver specialist has informed you that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection, and that he wants to run additional blood work so he can learn more about your HBV. Some of this blood work may need to be repeated over a period of time, but over the next 6 months or so, your doctor will determine whether or not you are a good candidate for treatment. Regardless, he will definitely want to continue monitoring. Remember, treatment is important, but rarely an emergency, so be patient.
Now you need additional lab work to determine your HBe status, which will tell you whether or not you are HBeAg and HBeAb (anti-HBe) negative or positive. This reveals a great deal about your HBV such as whether or not the virus is replicating, and how infectious you are to others.
At this point, it is helpful to have a little background on antigens and antibodies. An antigen is a foreign substance in your body that evokes an immune response. This may include viruses, bacteria or other environmental agents such as pollen or a chemical. In this case, it is the HBV e antigen. Your previous hepatitis B panel tested for the surface antigen, or HBsAg.
Antibodies are produced as a result of an immune system response to antigens. These antigen/antibody pairings are unique. An antibody response can be generated as a result of an immune response to an actual infection, or as a result of vaccination. An uninfected person vaccinated against hepatitis B will generate an immune response, or surface antibody (HBsAb, or anti-HBs) to the HBV vaccine.
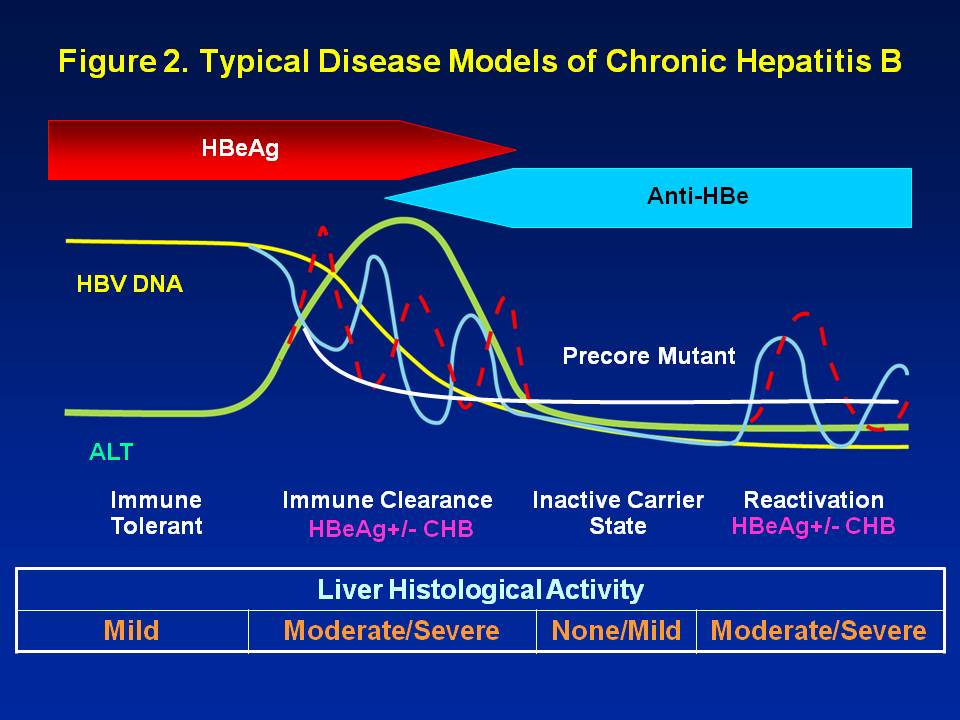
The hepatitis e antigen, or HBeAg, is a marker of an actively replicating HBV virus infection. Those with a positive HBeAg have active replication in their liver cells, more of the virus circulating in their blood, and as a result, they are more infectious, with a higher likelihood of transmitting HBV to others. Most often, when a person is HBeAg positive, they tend to be HBeAb negative and vice-versa. This active, replicating phase may go on for weeks, as in the case of an acute infection, or for years, or even decades in those chronically infected.
Eventually most move into a non-replicative stage. During this time, e antigen (HBeAg) is no longer in the blood, and the anti-HBe antibody (HBeAb) is generated and appears in blood work. This HBeAg serconversion, or loss of HBeAg and the gaining of the antibody, HBeAb, can happen due to treatment, or spontaneously without treatment. Entering this stage is typically a good thing, and is often a goal of treatment. However, monitoring by your liver specialist bi-annually or at least annually is essential, even if you have had an HBeAg serconversion years ago and are considered in the non-replicative phase.
HBV is complicated, and sometimes you may relapse. In other words, you may seroconvert losing HBeAg and gaining the HBeAb antibody, but it may not be durable, and you may have an HBeAg reversion to an actively replicating stage where you are once again HBeAg positive and HBeAb negative. Years ago they called it “flip-flopping”. This possibility is one of many reasons why regular monitoring by your liver specialist is so important.
The other possibility is the development of HBe-negative hepatitis B, which is the result of hepatitis B mutations. These precore or core promoter mutations replicate without generating the HBe antigen. However, they are actively generating the virus, though typically not at the levels of those with HBeAg positive HBV. Once again, it is critical to continue regular monitoring by your liver specialist, so you are sure you have not begun active generation of HBe negative mutations.
Additional blood work ordered by your liver specialist will further clarify your HBeAg and over-all HBV status, and whether or not treatment may benefit you.
More next time…