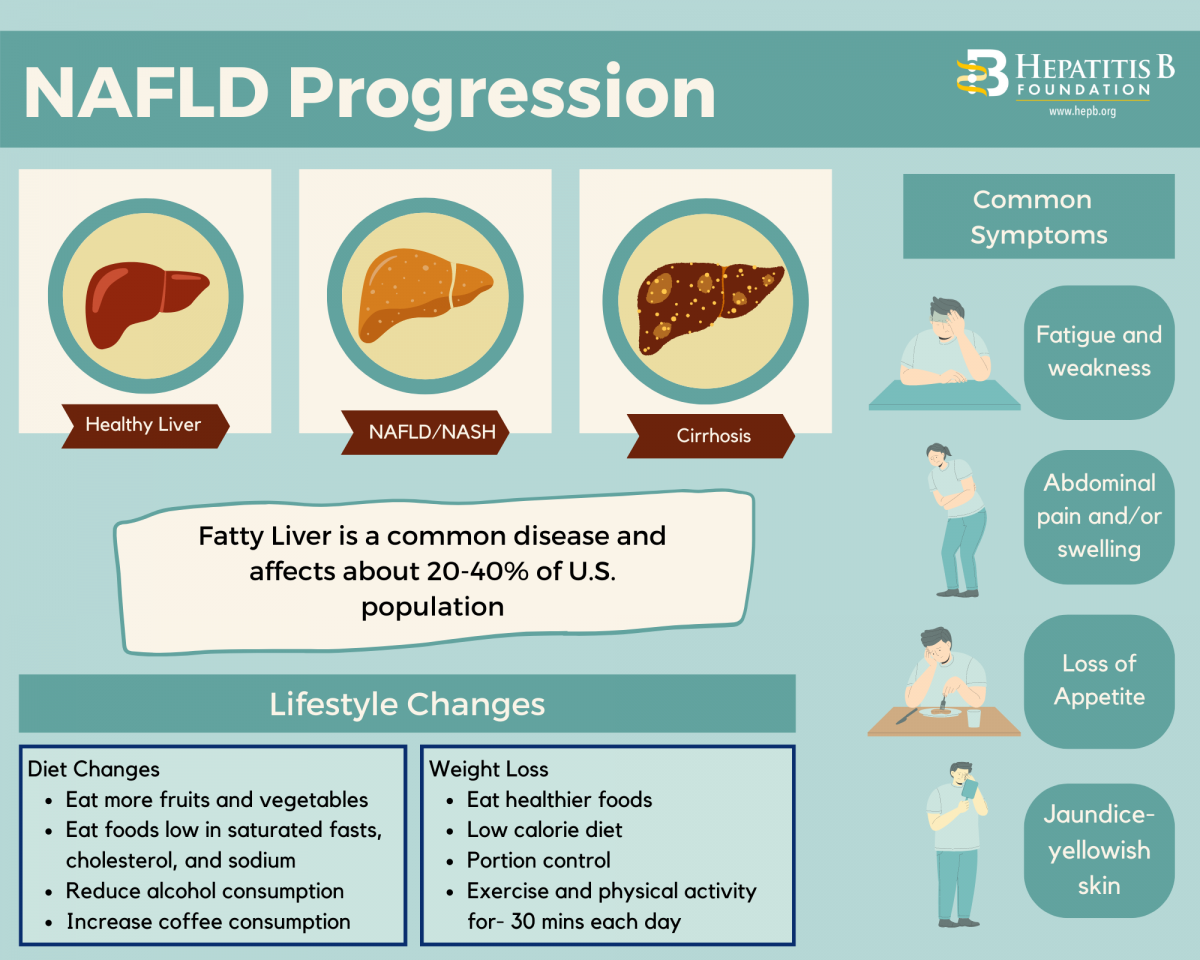
The Coalition Against Hepatitis for People of African Origin (CHIPO) is a national community coalition that is co-founded and led by the Hepatitis B Foundation, comprised of organizations and individuals who are interested in addressing the high rates of hepatitis B infection among African communities in the US. Recently, CHIPO has started to expand its reach to communities in Africa and has welcomed new partners from the Continent. This month, in honor of Minority Health Month, we highlight a partnership between CHIPO and Great Lakes Peace Centre (GLPC) in Kasese, Uganda. CHIPO has recently provided GLPC with educational resources that are tailored for African communities, which GLPC is translating into local dialects and will use in a strategy to raise awareness and provide education about hepatitis B, primarily to rural women and youth in Kasese District. A recent interview with Bwambale Arafat, Head of Health and Policy Officer at GLPC, sheds light on some of the significant barriers that impede hepatitis B screening, prevention, and care in Uganda (and much of the African continent) and showcases some of the extraordinary work of GLPC on a host of issues, of which viral hepatitis is just one.
CHIPO: Can you share a little bit about yourself? What is your connection to hepatitis?
Arafat: I work with the Great Lakes Peace Centre, which is a grassroots, youth-led organization, here in Kasese District, a rural area in Rwenzori region, western Uganda (near the border of the Democratic Republic of Congo, about 400 kilometers from the capital city of Kampala). Most of our work with hepatitis B is focused on raising awareness and providing education about the virus to women and youth in the area, who are the most important people to reach. We also engage in a lot of advocacy initiatives, as well as efforts to lower stigma and discrimination.
My personal connection to hepatitis B is the diagnosis of my uncle with hepatitis B and liver cancer and his death shortly thereafter. There was widespread misconception that he had been bewitched and poisoned by relatives. I have been working to try to dispel some of these myths and provide accurate information ever since. In 2021, I was honored as a World Hepatitis Alliance champion for hepatitis outreach work during COVID-19. I and GLPC are deeply committed to the cause of hepatitis B elimination by the year 2030.
CHIPO: Congratulations on the well-deserved honor! Can you share a bit about the work and goals of your organization?
Arafat: Due to its proximity to the Democratic Republic of Congo, Kasese feels the effects of war and conflict acutely, and the area is quite fragile. Peace and Conflict Resolution is the first of three priority areas for GLPC and is driven forward by the efforts and demographic dividends of young people. Health Promotion and Public Policy is the second priority area, which encompasses awareness and education about hepatitis, HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis prevention, screening, and treatment, as well as nutrition assessments, counseling, and support, especially for mothers of children under five years of age. Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene is another topic of top concern, and initiatives in this sector included a hand-washing campaign for COVID-19. The last focus area under the Health Promotion umbrella is adolescent sexual and reproductive health, and especially promotion of education equity for menstruating young women and ending of stigma and discrimination around this, thus keeping young women in school for longer. Social empowerment happens through education, and people can donate to keep girls in school with financial support. The third organizational priority is to focus on climate change – GLPC distributes solar panels through public and private partnerships, as a great step toward sustainability and protecting the planet we share.
CHIPO: What are some of the biggest barriers to hepatitis screening, prevention, and care in your community?
Arafat: As I mentioned above, the widespread presence of myths and misconceptions about hepatitis B, especially about transmission, is one of the biggest culprits in perpetuating the stigma and discrimination that still dominate the hepatitis B conversation and presents one of the biggest challenges to increasing screening and vaccination. Some ways that we are working to dispel some of these misconceptions are through our social media platforms, which all have huge followings by younger people. However, attitudes are very slow to change, and this is why the involvement of religious and community leaders in spreading accurate information and shifting the narrative around viral hepatitis is so important, and why personal testimonials and connections with people who are living with hepatitis B hold such power.
Other challenges to screening, prevention, management, and treatment of hepatitis B in Kasese include the enormous out-of-pocket costs of diagnosis and testing; the persistent lack of awareness among the general population – primarily lack of information, education, and communication; the lack of logistics and supplies for things like test kits and cold chain storage for vaccines; and the long distances and mountainous topography that make access to health facilities in larger cities difficult. Additionally, funding and resources from the government and other stakeholders remain inadequate, making it difficult to ensure that services will be available when they are needed. The Minister of Health and government of Uganda have created infrastructure to help with vaccination (they have provided 1 million USD for this reason), have recommended universal adult vaccination, and have also waived fees for viral load investigation. However, things like ultrasound scans, complete blood count panels, and other tests to determine when someone would need treatment for hepatitis are not subsidized. The government could also do a great deal more in terms of increasing awareness, investing money into management and care, prioritizing the birth dose of the vaccine to prevent mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B, and addressing the stigma and discrimination so many living with hepatitis B routinely face.
Many infants also continue to be delivered by traditional birth attendants, who are not trained in preventing mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B, and knowledge among community health workers in general is very low. There is also inadequate data and surveillance of the disease, and no records of screening, vaccination, or care are kept in the Health Management and Information System. There is a lack of clear guidelines around testing for the medical community and a lack of materials that can help to raise awareness and combat stigma.
We also really need to integrate hepatitis services into those that exist for HIV/AIDS. Machines that are used to test for HIV/AIDS can be recalibrated to also test for hepatitis. Electronic Health Records can be upgraded to include hepatitis B status. As awareness grows, patients can also hold health workers accountable for hepatitis testing, as they do now for HIV and syphilis. This conversation needs to start with the people themselves.
CHIPO: How are you planning to use CHIPO’s materials and resources over the next year?
Arafat: We have a saying in Kasese: “When you talk in a foreign language, you talk to people’s heads. When you speak in their language, you speak to their hearts.” Our first priority is to translate CHIPO’s flip charts, takeaway cards, and guides for health educators into our local dialects of Lhukonzo and Runyakitara, in order to reach as many community members and stakeholders as possible. We will host four community educational events using the materials and in these events, will focus on hepatitis B overview, causes and prevention, common myths and misconceptions, and unmet needs in this area. These sessions will be moderated by NoHep Champions and Hepatitis Ambassadors, so that the community can hear from people with direct experiences of the disease and their voices can be amplified.
Additionally, we will host NoHep Champion Table Talks, which are informal discussions that will consist of young people living with HBV and pregnant women, who will share stories and build community. These talks will touch upon how people are doing physically, as well as with handling stigma, and will identify needed services, insights which can help to determine future programming and practices. These talks will also emphasize that no one is alone, and that hepatitis B is not a death sentence, but that people with HBV can live long and healthy lives. We will also convene community barazas (gatherings) with local leaders, including social workers, health workers, village health teams, hepatitis ambassadors, local council, and cultural, community, and religious leaders to conduct trainings on delivery of the educational materials. These will provide an opportunity to educate and invite open discussion. We will also hold continuing education courses on hepatitis B for healthcare professionals at health facilities, including community health workers, village health teams, and para-social workers. Finally, we are planning to compose a radio jingle related to hepatitis B that will be heard around the district.
Only 1 in 10 people in Kasese know their hepatitis B status. These materials can go a long way in changing that.
CHIPO: Thank you so much for your valuable insights and for all of the work you are doing! Do you have any final thoughts or messages that you would like to share?
Arafat: I would just like to mention our No Hep Mamas campaign, which we are also implementing for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B. We are working to bring this campaign to more health facilities, and share this information in prenatal care settings, as stopping the cycle of transmission is truly the best way to eliminate hepatitis B.
CHIPO: Thank you so much again for your time today, Arafat, and we look forward to more inspiring work from you in the future!
Arafat: Thank you very much!