Part I discussed how hepatitis B is transmitted and may have helped you determine how you were infected with hep B. In Part II we will discuss the people closest to you who may be susceptible to your infection.
Part I discussed how hepatitis B is transmitted and may have helped you determine how you were infected with hep B. In Part II we will discuss the people closest to you who may be susceptible to your infection.
Anyone exposed to Hep B is susceptible. This is true if you have not already been vaccinated, or are not taking precautions. Hep B does not discriminate. However, those most susceptible to infection are your sexual partners, close household contacts or family members. Why are the these people more susceptible? Remember that HBV is transmitted through direct contact with blood and sexual fluids, so sexual partners will be at risk. Unfortunately even close contacts without sexual intimacy may also be at risk. These include family members or roommates that might borrow your razor, the nail clippers on the downstairs counter, or your favorite pair of pierced earrings or body jewelry. Such personal items may have trace amounts of blood on them. All you have to do is keep them separate until everyone is tested and vaccinated.
Hepatitis B is NOT spread casually. You will not get HBV by co-existing in the same house, sharing a meal or eating food prepared by someone with hepatitis B. You will not get hep B by sneezing, kissing, hugging or holding someone with hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B can live outside the body for a week. It just makes sense that the odds of an exposure are more likely with someone you live with just due to the increased potential for daily exposure in simple grooming routines or household activities where blood could be exchanged. The good news is that hep B is preventable.
It is important to know that unvaccinated babies and young children are more susceptible to Hep B. In fact 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children infected with hep B will have life-long infection. This is a complicated topic, but basically their immune systems are immature. That is why young babies and young children may have high viral loads, but usually less damage. The immune system gets tricked and the virus replicates unchecked in liver cells. That is why hepatitis B vaccine series, starting with a birth dose, is so important for babies and young children.
So what should you do? You need to do the right thing. You need to talk to sexual partners and close contacts and family members now that you know you are infected. You don’t need to tell everyone; just those that you believe are at risk. Tell them to ask their doctor to run a hepatitis B panel.
The hepatitis B panel is one blood test with 3 parts: HBsAg – surface antigen; HBcAb – core antibody; and HBsAb – surface antibody. When read in combination, this one test can tell your close contacts if they are currently infected, have recovered from a previous infection, and whether or not they have immunity to the hepatitis B virus. Typically the blood test results are straight forward, but sometimes they can be tricky. Ask those tested to discuss their results with their doctor, and to keep a copy of the blood tests results for later review.
One important factor for those that may have been exposed is the timing. There is up to a 9 week window period between an exposure to hep B and when the hepatitis B virus shows up in the blood resulting in a positive test result. If you tell your partner and they insist on immediate testing, they need to understand that they will need to be re-tested 9 weeks later to ensure whether or not they have been infected. AND, it is essential to practice safe sex and follow general precautions until everyone is sure of their status –both the known and potentially infected.
Remember you may still be in a waiting period trying to determine if you are acutely or chronically infected. Very possibly you have not had symptoms with your hep B. Nearly 70% of those with newly infected with HBV have no notable symptoms. It’s also very likely you are unsure when you were infected. And of course it’s possible you are chronically infected and have had hep B for quite some time. It’s stressful and little confusing not knowing the details of your infection, but you need to move forward doing the right thing and talking to those at risk and taking care of yourself.
Take a look at Part I and Part III for further discussion of hep B transmission.


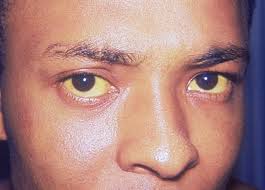 The tricky part about
The tricky part about