The hepatitis B virus (HBV) can be transmitted two ways: 1) through direct contact with blood and 2) infected body fluids. Some risks for direct blood contact are obvious, such as touching an open wound to another open wound or cleaning up someone’s blood without any protective gear. However, other methods of blood transmission are harder to catch. Common activities like sharing razors, earrings, or toothbrushes are simple, innocent actions, yet they all have the potential for blood exchange.
Medical and dental procedures are aspects of our lives that we might not think twice about. While beneficial to our health, they also carry the risk of exposure to another person’s blood. Surgeries, shots, and dental activities all use sharp objects that pierce the skin and draw blood. If the tools are not properly sterilized, or cleaned, before they are used on a new patient, the blood that was on the equipment can be transferred to the next patient.
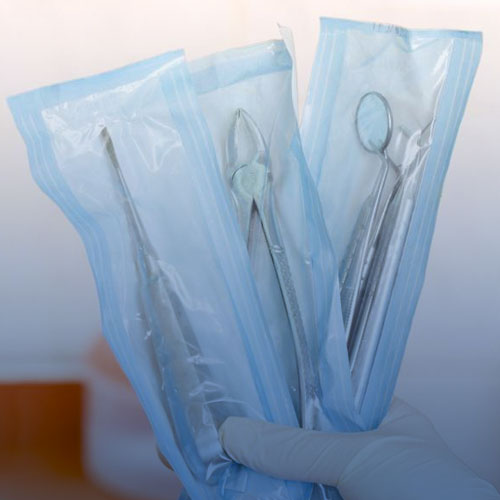
How do I know if medical tools are sterile? Ask! It is your right to know if the equipment that will touch your body has been thoroughly cleaned. In a dentist office, the assistant might unwrap a package of tools in front of you; this typically means that the tools are either new or have been properly cleansed. In a medical setting, needles and surgical equipment might come in packaging as well. If you still are not certain, feel free to ask what the standard cleaning procedures are for the tools being used. The staff will be happy that you are taking your health into your hands!
Why is it important to have sterile tools? Hepatitis B earned the nickname “silent infection” because there are often no symptoms. Those who have been infected may not take the necessary precautions simply because they do not know that they should. They may not even know they are infected! In many cases, medical and dental professionals are unaware when a patient has hepatitis B. Therefore, it is important to make sure that all equipment that is being reused has been sterilized. Although there are no global sterilization standards, many countries and medical facilities around the world – like hospitals, dental offices, and doctor offices – have disinfection guidelines and practices for their equipment.
Tips to Protect Yourself:
- Be your own advocate: Ask the dental hygienist, nurse, doctor, acupuncturist or person in charge of your procedure if the tools have been sterilized.
- Know where you go: Try to visit medical or dental facilities that you trust and that provide clean, safe environments for any procedures involving blood or body fluids.
- Get vaccinated: Hepatitis B is a vaccine preventable disease. After receiving all three doses, most people are protected for life! Check your immunization records to make sure that you have been vaccinated or ask your doctor or local clinic about the vaccine.
- Share with caution: Sharing or eating food prepared by someone with hepatitis B is safe, but any activities that may involve direct contact with blood carry a risk. A good guideline is to keep all personal hygiene items personal.
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, it is important to get tested. Visit your doctor or local health clinic to get screened.
If you have been diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, our Physicians Directory* can help you locate a liver specialist near you. The World Hepatitis Alliance can also help you find health care services and hepatitis B education in your country.
*Disclaimer
The Hepatitis B Foundation Liver Specialist Directory is intended for use by the public to assist in locating a liver specialist within a specific state or country. All data is self-reported and is not intended for use by organizations requiring credentialing verification. The HBF does not warrant the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, or appropriateness for a particular purpose of the information contained in the Liver Specialist Directory. The HBF does not endorse the individuals listed in the service, nor does HBF verify medical qualifications, licenses, practice areas or suitability of those listed. In no event shall the HBF be liable to you or anyone else for any decision made or action taken by you based upon the information provided in the service. Note: This is not a physician referral service. The HBF cannot provide referrals to specific physicians nor advice on individual medical problems.

