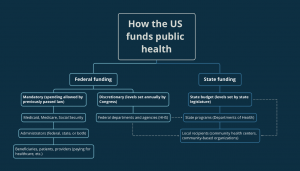
The Coalition Against Hepatitis for People of African Origin (CHIPO) is a community coalition that is co-founded and led by the Hepatitis B Foundation and is made up of organizations and individuals who are interested in addressing the high rates of hepatitis B infection among African communities in the U.S. and globally. Over the past year, CHIPO has grown its membership to include over 50 community-based organizations and federal agencies, all of which are working to meet the common goals of raising awareness about hepatitis B among African communities, and increasing rates of screening, vaccination, and linkage to care. This month, we are excited to highlight the work of one of our partners, the Hepatitis B Initiative of Washington, DC, (HBI-DC), and their new Deputy Executive Director, Sandra Ashford. Please enjoy a recent interview with Sandra, as she describes her work, including successes and challenges, and the positive impact HBI-DC has had by expanding their organization and mission.
Could you please introduce yourself and your organization?
Hello, my name is Sandra Ashford. The current Deputy Executive Director for the Hepatitis B Initiative, Jane Pan, will soon be retiring, and I’ll be stepping into the role. I started out in hepatitis B as a Latino outreach coordinator and then worked with the Fairfax County, Virginia, health department. I have also worked with IPHI (Institute for Public Health Innovation) for COVID.
Can you tell me about HBI-DC?
HBI-DC was founded by Leslie Oh, whose mom and brother died in the same year of hepatitis B-related complications. After experiencing the pain of losing her family members she decided that she did not want anybody else to go through that struggle. As a result, she started HBI Boston, where she was studying public health at Harvard University at the time. While in school she would pass out informational pamphlets about hepatitis and engage in other advocacy efforts. She moved to Washington D.C. in 2006 and started HBI-DC, which is where our organization started and from where it continues to grow.
Could you tell me about what some of HBI-DC’s programs are that specifically address hepatitis and other health concerns in African communities?
The programs that we offer include free health screenings for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV, as well as free glucose and cholesterol screenings for the community. Our reach at HBI-DC includes individuals in Washington DC, Maryland, and Virginia and, since 2006, we have educated 80,000 individuals on hepatitis, and have screened 24,000 people for hepatitis B, and an additional 22,000 for hepatitis C. From these screenings, 1,100 people have tested positive for hepatitis B and 900 people for hepatitis C. For us, that is a big success because those are individuals who did not know they were living with hepatitis.
Our programs target high-risk individuals including immigrants, especially from Africa and Latin America. Any individuals who test positive for hepatitis B or C are linked to free health care, thus ensuring that follow-up and support are established, and people are not left alone with a positive hepatitis B or C diagnosis. We also provide health education in the native language of our clients, so that everybody is accounted for in these different communities.
Which countries are primarily represented in the African diaspora that HBI-DC serves?
The African communities that we have served so far based on our screenings and education activities come from Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina, Cameroon, Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Guinea, Libya, Liberia, Morocco, Nigeria, and Sierra Leone.
What are some of the biggest challenges in addressing hepatitis and other health concerns at the community level? How have you worked to overcome these? Are there any additional resources that would be helpful to have?
A significant challenge we encounter at the community level is health misinformation. Social media platforms have contributed to the mistrust of providers and vaccine mandates, and there is a significant lack of knowledge regarding viral hepatitis. We overcome these challenges through a diverse and multilingual workforce. Our community is more receptive to testing and education if they feel like they’re speaking to a representative that looks like them, shares cultural experiences, and speaks their language. In addition, all our educational and preventative material is also translated into different languages. We also utilize social media channels targeted at these diverse communities to spread accurate information on hepatitis and target populations most at risk.
What do you think are some of the biggest barriers in raising awareness and addressing rates of hepatitis screening and linkage to care at the local, state, and federal levels? Do you think more could be done in these spheres to address this problem?
A big barrier for us is the stigma associated with HIV and hepatitis. For this reason, when we go out to events and we’re talking to communities we try to offer comprehensive health services like cholesterol and glucose screenings. When individuals get glucose and cholesterol screenings, it gives us an opportunity to educate the clients on HIV and hepatitis, because we understand the stigma associated with these diseases. Another barrier is just overall awareness and education, but we try to develop trust in the community to overcome this. Once this trust is built, it’s easier for the community to be receptive to our services and educational messaging.
I think the digital divide is a major challenge facing African immigrant communities, which can affect all aspects of their health and healthcare. When we started outreach efforts during the COVID-19 pandemic, we wanted to keep in touch with a lot of the clients that we had tested and helped out just to see how they were doing. One thing that we saw was that there was a lack of digital skills and knowledge. For example, these communities were asking us for assistance in obtaining unemployment. Of course, we’re there to help them and to walk them step by step through the process but this lack of knowledge in the digital space was a big issue in connecting them to public health assistance programs during this time. This technological burden relates back to issues of connecting care in the community especially as they pertain to awareness, education, and linkage to social services. I think that overall, this traces back to social determinants of health, so I think more education and more support for the community are needed to address these concerns.
What are your favorite parts about your job? What got you interested in this work?
I started in public health with HBI, and the one thing I love is the challenge. It’s every day you’re coming in and there’s something that needs to be addressed or you are making an impact in a certain community and coming up with solutions. I think those are the best parts of being an executive director, knowing the impact you have on communities. The best story I can share is about when I was a Latino outreach coordinator, and we were screening for glucose and cholesterol. This one gentleman tried to come in numerous times and finally, we got him in for a screening. He was losing a lot of weight and couldn’t sleep at night, and he didn’t know it at the time, but when we tested him, he was diabetic. He was completely unaware because he had no healthcare access, and after the event, he went to the emergency room to receive care. He told us if it wasn’t for us, he could have died, and he said HBI-DC was like an angel to him. We also connected him with a great nonprofit clinic, La Clinica del Pueblo in D.C., and they were able to get him health insurance. Today he’s on health insurance and medication and doing well.
Any other thoughts or ideas you’d like to share for improving health and closing health disparities among African immigrant communities in the U.S.?
I think some suggestions are to continue building community health worker programs. I think they make a big impact, especially regarding trust within the community and addressing the social determinants of health. I think we can reach out to more individuals in the Latino community and the African immigrant community and encourage them to take part in these programs. I believe support for these programs is important in closing health disparities. Also, I would avoid duplication of efforts to also achieve the greatest impact. So overall, utilizing our diverse partnerships to offer health services and close health disparities is the next step forward to reaching at-risk populations in the community.
Thank you so much for taking the time today, Sandra, and for sharing more about the amazing work HBI-DC has done in the community and will continue into the future!
Thank you!